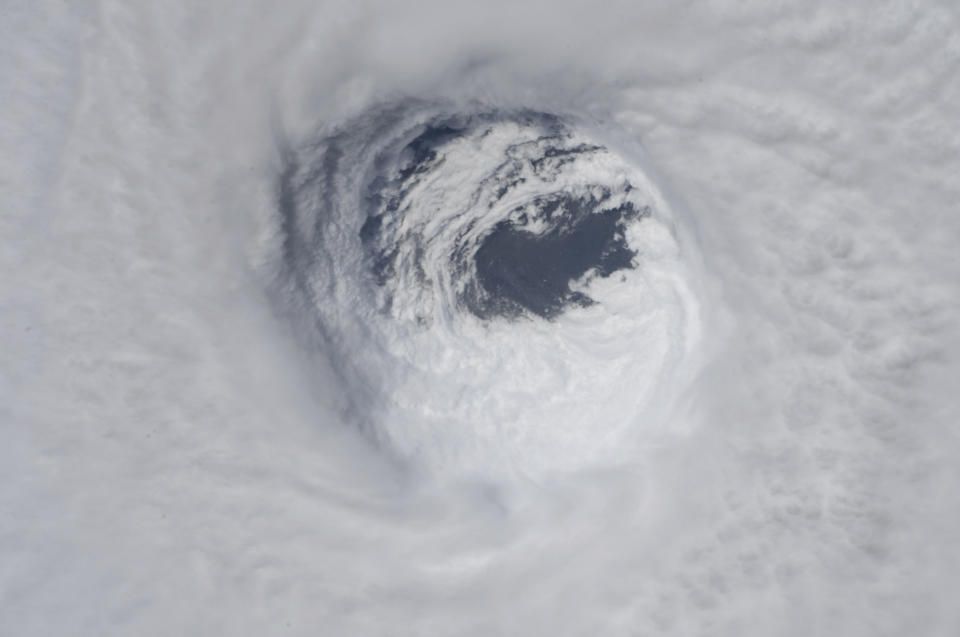
Supercharged by abnormally warm waters in the Gulf of Mexico, Michael slammed into the Florida Panhandle on Wednesday with potentially catastrophic winds of 155 mph, the most powerful hurricane to hit the U.S. mainland in nearly 50 years.
Michael blew ashore near Mexico Beach, a tourist town about midway along the Panhandle, a lightly populated, 200-mile stretch of white-sand beach resorts, fishing towns and military bases.
Its winds roaring, it battered the coastline with sideways-blown rain, powerful gusts and crashing waves. It swamped streets, bent trees, stripped away limbs and leaves, knocked out power, shredded awnings and sent other building debris flying. Explosions apparently caused by blown transformers could be heard.
“The window to evacuate has come to a close,” Federal Emergency Management Agency administrator Brock Long said.
The meteorological brute quickly sprang from a weekend tropical depression, becoming a furious Category 4 by early Wednesday, up from a Category 2 less than a day earlier. It was the most powerful hurricane on record to hit the Panhandle.
“I’ve had to take antacids I’m so sick to my stomach today because of this impending catastrophe,” National Hurricane Center scientist Eric Blake tweeted as the storm — drawing energy from the Gulf’s unusually warm, 84-degree water — grew more scary.

National Hurricane Center director Ken Graham, center, gestures while updating viewers on the status of Hurricane Michael as National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration public affairs officer Dennis Feltgen holds the camera during a Facebook Live update, Wednesday, Oct. 10, 2018, at the Hurricane Center in Miami. (AP Photo/Wilfredo Lee)
Based on its internal barometric pressure, Michael was the most powerful hurricane to blow ashore on the U.S. mainland since Camille in 1969. Based on wind speed, it was the fourth-strongest, behind Andrew in 1992, Camille, and the biggest one of all, an unnamed 1935 Labor Day storm that had winds of 184 mph (296 kph).
More than 375,000 people up and down the Gulf Coast were urged to evacuate as Michael closed in. But emergency authorities lamented that many people ignored the warnings and seemed to think they could ride it out.
“While it might be their constitutional right to be an idiot, it’s not their right to endanger everyone else!” Walton county Sheriff Michael Adkinson tweeted.
Diane Farris, 57, and her son walked to a high school-turned-shelter near their home in Panama City to find about 1,100 people crammed into a space meant for about half as many. Neither she nor her son had any way to communicate because their lone cellphone got wet and quit working.
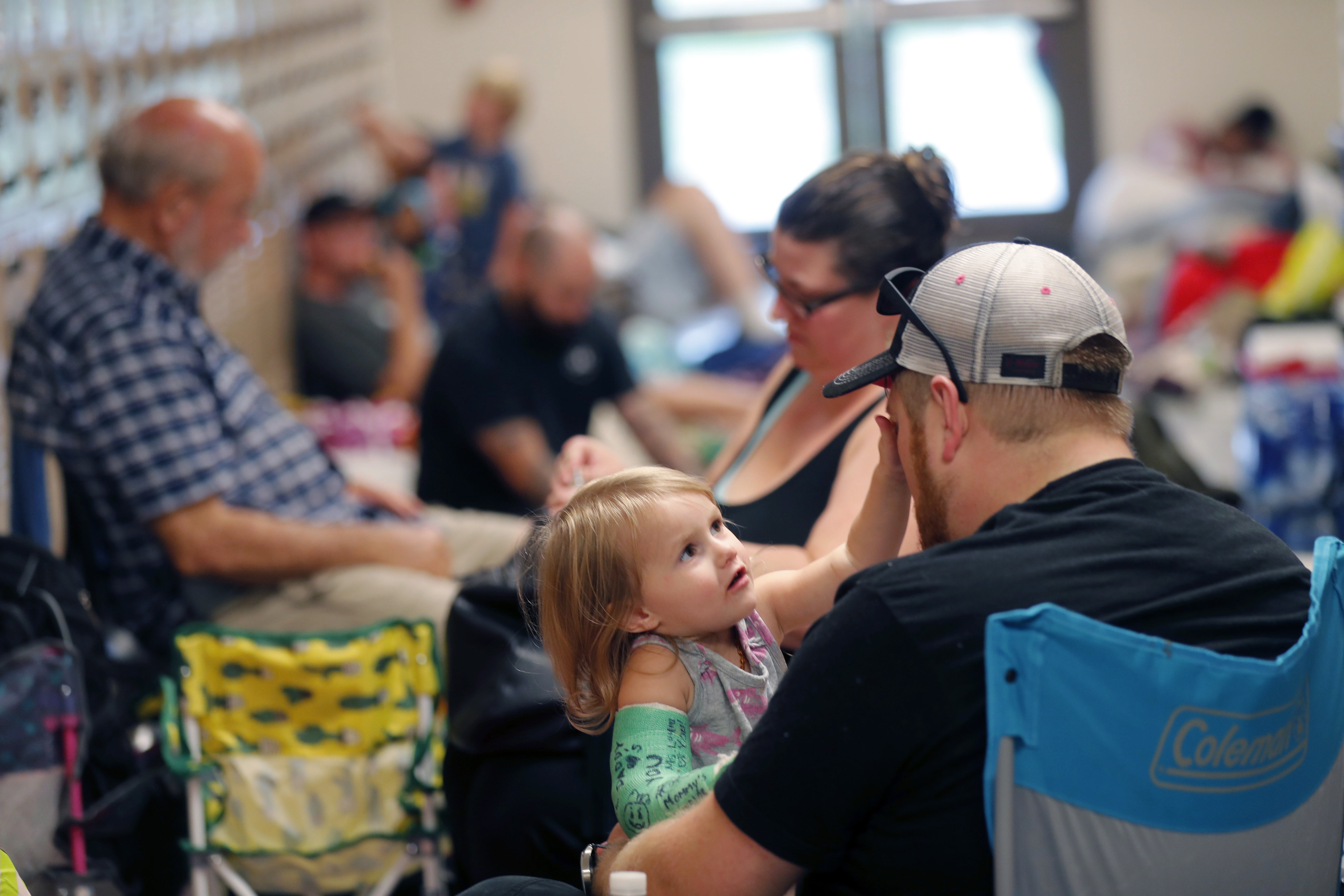

Sean Pelham holds his daughter Sophia, 2, in a hallway at an evacuation shelter set up at Rutherford High School in advance of Hurricane Michael, which is expected to make landfall today, in Panama City Beach, Fla., Wednesday, Oct. 10, 2018. (AP Photo/Gerald Herbert)
“I’m worried about my daughter and grandbaby. I don’t know where they are. You know, that’s hard,” she said, choking back tears.
Hurricane-force winds extended up to 45 miles (75 kilometers) from Michael’s center. Forecasters said rainfall could reach up to a foot (30 centimeters), and the life-threatening storm surge could swell to 14 feet (4 meters).
The storm appeared to be so powerful that it is expected to remain a hurricane as it moves over Georgia early Thursday. Forecasters said it will unleash damaging wind and rain all the way into the Carolinas, which are still recovering from Hurricane Florence’s epic flooding.
Meteorologists watched satellite imagery in complete awe as the storm intensified.
“We are in new territory,” National Hurricane Center Meteorologist Dennis Feltgen wrote on Facebook. “The historical record, going back to 1851, finds no Category 4 hurricane ever hitting the Florida panhandle.”

A storm chaser climbs into his vehicle during the eye of Hurricane Michael to retrieve equipment after a hotel canopy collapsed in Panama City Beach, Fla., Wednesday, Oct. 10, 2018. (AP Photo/Gerald Herbert)
Colorado State University hurricane expert Phil Klotzbach said in an email: “I really fear for what things are going to look like there tomorrow at this time.”
Scientists say global warming is responsible for more intense and more frequent extreme weather, such as storms, droughts, floods and fires. But without extensive study, they cannot directly link a single weather event to the changing climate.
With Election Day less than a month away, the crisis was seen as a test of leadership for Scott, a Republican running for the Senate, and Tallahassee Mayor Andrew Gillum, the Democratic nominee for governor. Just as Northern politicians are judged on how they handle snowstorms, their Southern counterparts are watched closely for how they deal with hurricanes.
Hours ahead of landfall, seawater was already lapping over the docks at Massalina Bayou near downtown Panama City, and knee-deep water was rising against buildings in St. Marks, which sits on an inlet south of Tallahassee, Florida’s capital.
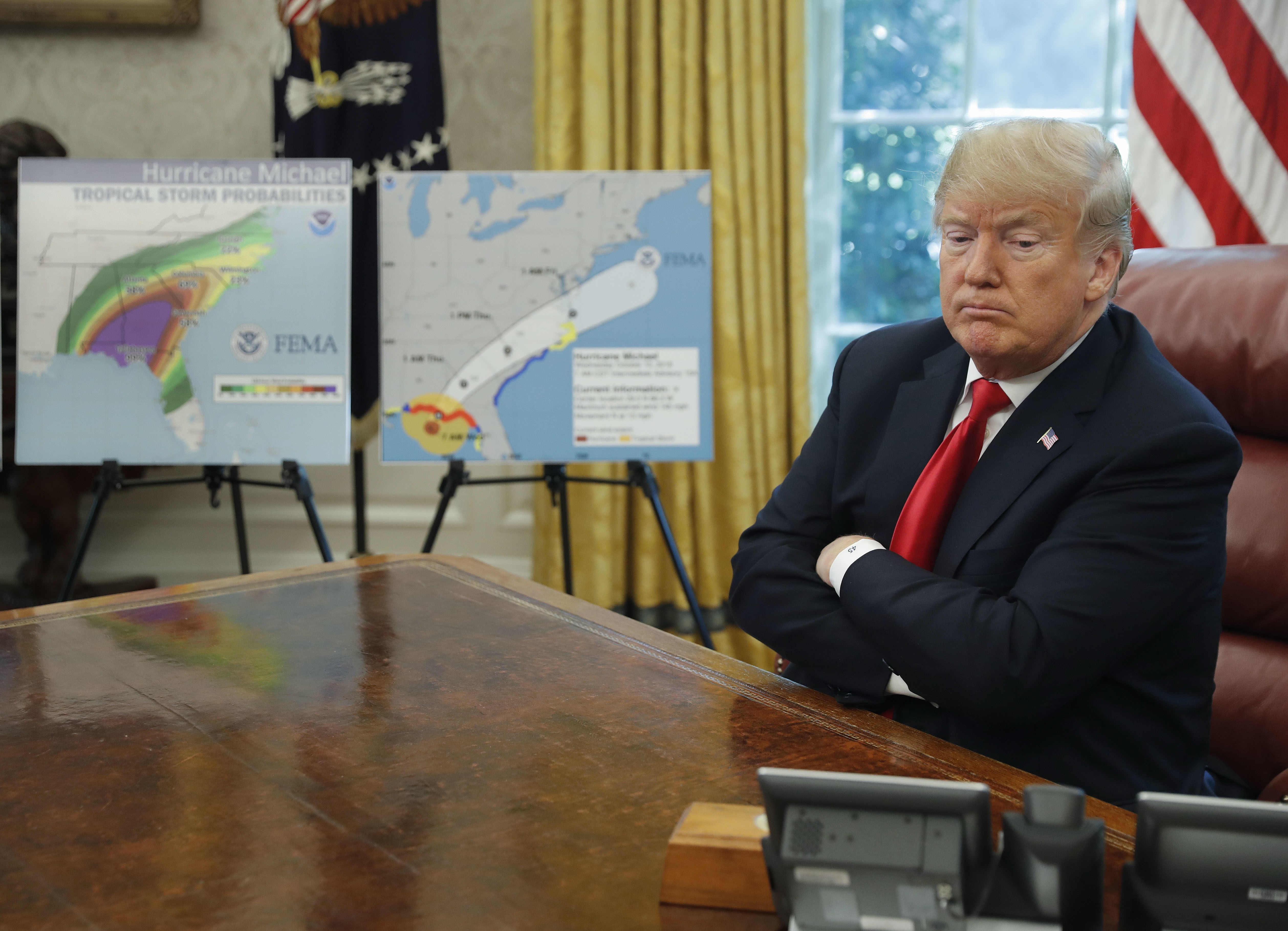

President Donald Trump pauses during his meeting to discuss potential damage from Hurricane Michael, in the Oval Office of the White House in Washington, Wednesday, Oct. 10, 2018. (AP Photo/Pablo Martinez Monsivais)
Huge waves pounded the white sands of Panama City Beach, shooting frothy water all the way to the base of wooden stairs that lead to the beach.
More than 5,000 evacuees sought shelter in Tallahassee, which is about 25 miles from the coast but is covered by live oak and pine trees that can fall and cause power outages even in smaller storms.
Only a skeleton staff remained at Tyndall Air Force Base, situated on a peninsula just south of Panama City. The home of the 325th Fighter Wing and some 600 military families appeared squarely targeted for the worst of the storm’s fury, and leaders declared HURCON 1 status, ordering out all but essential personnel.
The base’s aircraft, which include F-22 Raptors, were flown hundreds of miles away as a precaution. Forecasters predicted 9 to 14 feet of water at Tyndall.
Evacuations spanned 22 counties from the Panhandle into north-central Florida.
“We’ve told those who stayed to have their life jackets on when the storm comes,” Tress Dameron, Franklin County emergency management coordinator, told The News Herald in Panama City.
In St. Marks, John Hargan and his family gathered up their pets and moved to a raised building constructed to withstand a Category 5 after water from the St. Marks River began surrounding their home.
Hargan’s 11-year-old son, Jayden, carried one of the family’s dogs in a laundry basket in one arm and held a skateboard in the other as he waded through calf-high water.
Hargan, a bartender at a riverfront restaurant, feared he would lose his home and his job to the storm.
“We basically just walked away from everything and said goodbye to it,” he said, tears welling up. “I’m freakin’ scared I’m going to lose everything I own, man.”
___
Story by the Associated Press.
Meteorologist Mike Mihalik discusses what to expect from Hurricane Michael
Mike Mihalik is a Senior Meteorologist with Weatherworks. He spoke to CGTN’s Asieh Namdar about tracking Hurricane Michael’s path.
Meteorologist Regina Miller explains Hurricane Michael’s path
Regina Miller is a meteorologist at Accuweather. She shared the latest news on the storm with CGTN’s Elaine Reyes, from Accuweather headquarters in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania.
 CGTN America
CGTN America